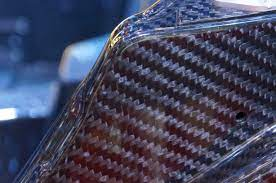
A composite material called fiber-reinforced plastic is made of a polymer that has had fibers added to it to enhance or add properties.
The most often used materials are glass or carbon fibers, however aramid, basalt, even wood and paper have been employed.
Fiber reinforced polymers are widely used in the construction, automotive, aerospace, and marine industries due to their low weight-to-strength ratio and resistance to corrosion.
Thermoplastic Fiber-Reinforced Plastics
Thermosets are more frequently used in fiber-reinforced plastics due to their lower cost, while thermoplastic resins have greater performance and can withstand temperatures of 400°F or higher. In addition, thermoplastics outperform thermosets in terms of compressive strength, toughness/damage resistance, hydrolysis, impact resistance, and vibrational damping.
4 Popular Fiber-Reinforced Plastics
Acetal: This powerful, low-friction
Engineering plastic provides powerful
wear characteristics and chemical resistance
both in dry and rainy situations.
It comes in glass-filled grades as well as
as well as a mix for PTFE-fiber reinforced
better lubrication
PEEK: For applications needing exceptional thermal, chemical, and combustion properties, PEEK is a good option.
Additionally, it has the highest thermal conductivity.
Nylon: Nylon is one of the most functional and widely used thermoplastic resins because of its superior physical characteristics and affordable price. Nylon is a material of choice for replacing metal gears due to its resilience to impact, corrosion, chemicals, and abrasion as well as its low coefficient of friction.
PTFE: A remarkable polymer with a broad operating temperature range, exceptional flexural strength, strong electrical resistance, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction against any known solid is PTFE, also known as Teflon®.
Additionally, PTFE is hydrophobic, chemically inert, and highly flexible. Pure PTFE deforms when loaded, hence fillers are routinely used to increase strength.
Advantages
- They can be easily drawn into fibers from molten state. Cheaper and readily available.
- Relatively strong.
- Chemically inert.
Disadvantages
- It has poor rigidity and stiffness.
- Its application is limited to a temperature below 300-degree Celsius.
The first step in developing a successful product is selecting the appropriate plastic. Our plastic specialists at Reading Plastic will assist you in selecting the best fiber-reinforced plastic for your application, then mill and build your components with precision to satisfy your tight-tolerance needs.