The textile industry can be a powerful driver of economic growth and development for a country, providing significant employment opportunities and contributing to GDP and export revenues. However, it also poses substantial challenges, particularly in terms of environmental impact, labor conditions, and economic vulnerability. Balancing these profits and disadvantages requires thoughtful policies and practices, such as enforcing labor laws, adopting sustainable production methods, and investing in worker welfare and environmental protection.
Benefits
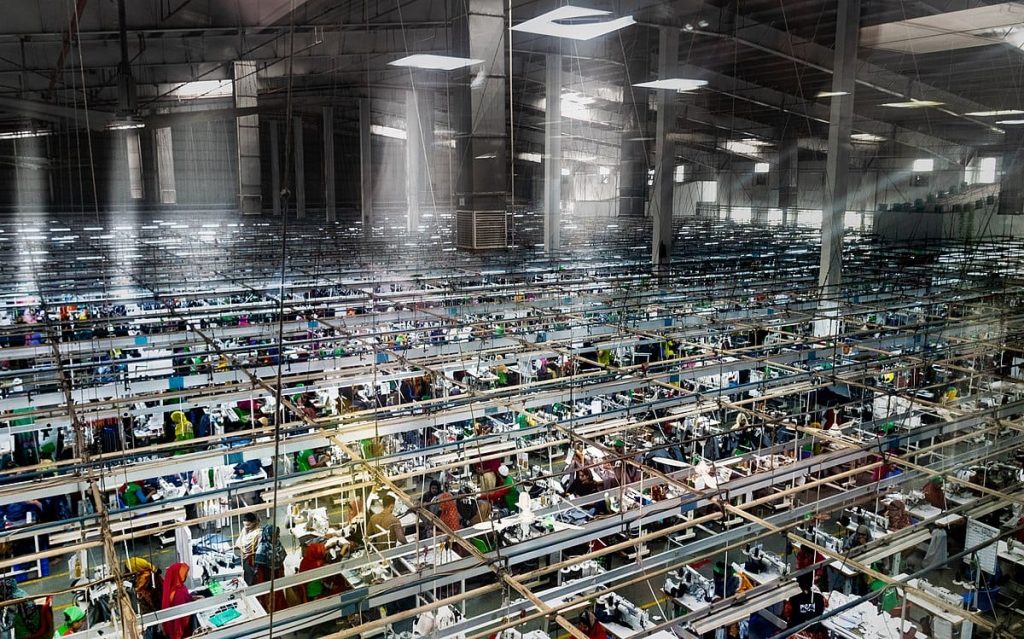

Economic Growth:
The textile industry is labor-intensive and can create numerous jobs, particularly in developing countries, thus reducing unemployment rates.
A thriving textile industry can significantly contribute to a country’s GDP through both direct and indirect economic activities.Textile products are major export commodities for many countries, generating substantial foreign exchange earnings.
Industrial Development:
The growth of the textile industry often leads to the development of related infrastructure, such as transportation, communication, and utilities. Investment in modern machinery and technology can boost productivity and efficiency within the industry.
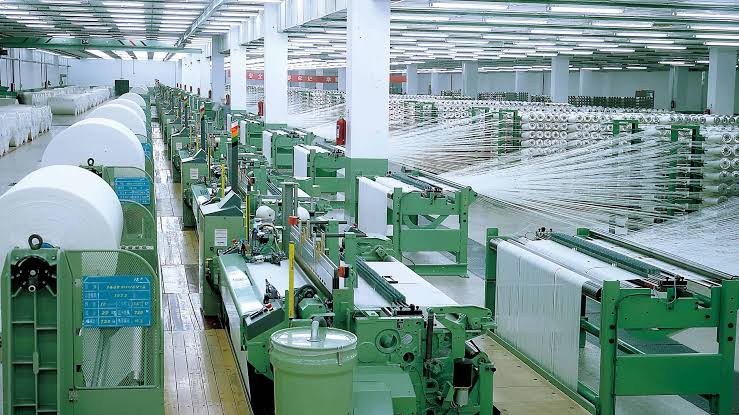

Value Addition:
The textile industry supports various sectors, from agriculture (cotton, wool, etc.) to fashion and retail, creating a comprehensive value chain.
Social Benefits:The industry provides training and skill development opportunities, improving the workforce’s qualifications and employability. Especially in developing countries, the textile industry often provides employment opportunities for women, contributing to gender equality and empowerment.
Disadvantages
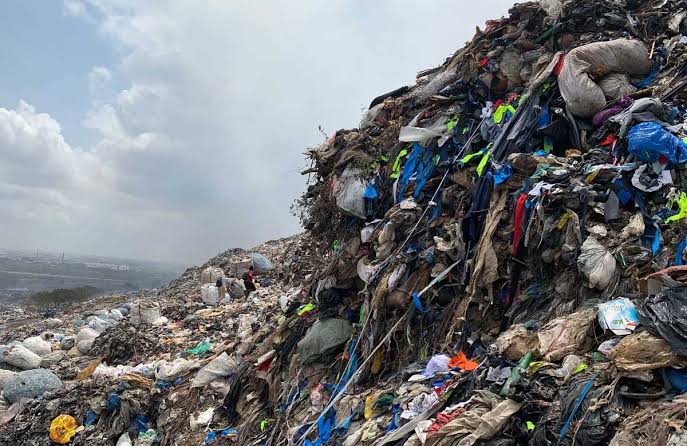

Environmental Impact:
Textile manufacturing can be resource-intensive and polluting, with issues like water and air pollution.
Labor Conditions:
Workers in textile factories, particularly in developing countries, often face poor working conditions and low wages.
Health Concerns:
Chemicals used in dyeing and finishing processes can be hazardous to workers’ health and the environment
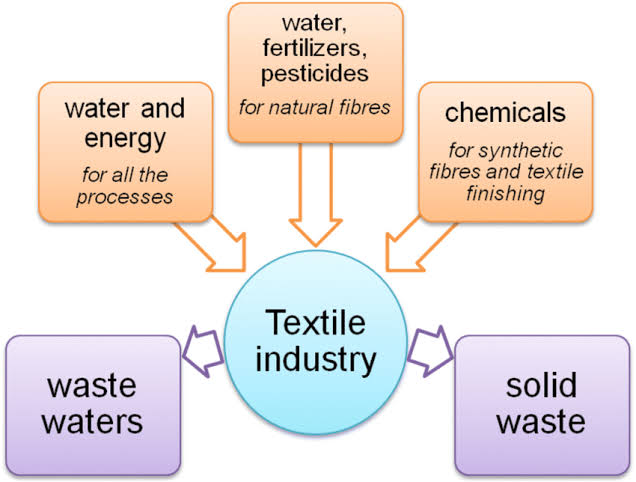
Waste Generation:
The industry generates significant waste, including textile scraps and packaging materials, contributing to landfill and environmental degradation.
Supply Chain Issues:
Complex global supply chains can lead to ethical concerns, such as labor exploitation and unsustainable sourcing practices.
Writer Information:

Ruhul Amin Siddiqee
Student, Textile Fashion and Design Department
Bangladesh University of Textiles (BUTEX)
Campus Team Member, Textile Engineers Society (TES).


