Machine used in Wet processing:
- Hank Dyeing machine: Hank dyeing is mainly done for carpet wool yarn dyeing. Besides, yarn for hand knitting and machine knitting is still predominantly dyed in hank form, although developments will allow these yarns to be package-dyed. Different types of hank dyeing machines include bobbin hank dyeing, cop hank dyeing, and cone hank dyeing.

Fig: Hank Dyeing machine
- Package Dyeing Machine: Package dyeing machines are the most widely used nowadays for dyeing almost all types of yarns, due to automatic, economical, and accurate dyeing results. Term package dyeing usually denotes for dyeing of any type of yarn wound on the compressible dye spring/perforated solid dyeing tubes or cones.

Fig: Package Dyeing Machine
- Beam Dyeing machine: A machine for dyeing yarns or fabrics that have been wound onto a special beam that has evenly perforated holes along its barrel. The dye is forced through the barrel into the yarn/fabric from inside to outside and vice versa. Beam dyeing is simply a much larger version of package dyeing. This method is similar to package dyeing but is more economical.

Fig: Beam Dyeing machine
- Jet dyeing machine: The jet dyeing machine is the most modern machine used for the dyeing of polyester fabric with dispersed dyes. In these machines, both the fabric and the dye liquor are in motion, thereby facilitating faster and more uniform dyeing. In the jet dyeing machine, there is no fabric drive reel to move the fabric.
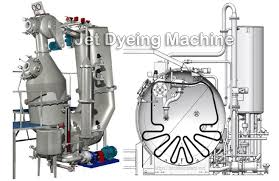
Fig: Jet dyeing machine
- Jig dyeing Machine: The Jig or jigger dyeing machine is one of the oldest machines used for cloth dyeing operations. Dyes are used for dyeing fabric in a Jig or Jigger dyeing machine which is suitable for woven fabric than knitted fabric because a jigger exerts considerable lengthwise tension on the fabric. This is also particularly suitable for cellulosic fibers because the natural dyes generally do not exhaust well and the jig works with an exceedingly low liquor ratio.
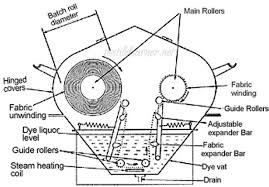
Fig: Jig dyeing Machine
- Paddle dyeing machine: Paddle Dyeing Machine. Paddle dyeing machines are generally used to dye many forms of textiles but the method is best suited to dye garments. Heat is generated through steam injection directly into the dye bath. The machine works like this, the paddle circulates both the bath and garments in a perforated central island.

Fig: Paddle dyeing machine
- Winch dyeing machine: The winch or beck dyeing machine is an old equipment used for processing fabrics in rope form. Besides, it is also the oldest form of piece dyeing machine. It is suitable for fabrics that can withstand creasing during rope form processing. In a winch dyeing machine, the fabric is processed in the form of an endless loop. Winch applies a low amount of tension on fabrics during processing. During processing, most of the fabric remains submersed in a deep trough which increases the material-to-liquor ratio (1:20 or 25) as compared to a jigger.

Fig: Winch dyeing machine
- Sample Dyeing Machine: The sample dyeing machine is to obtain satisfactory prescriptions for industrial production through proper staining and screening of dyes and auxiliaries. So, the sample dyeing machine will be equipped with the correct finishing machine. Infrared Heated Dyeing machine designed for dyeing small samples of Textile materials. Suitable for temperature and Atmospheric dyeing methods.

Fig: Sample Dyeing Machine
- Dip dyeing machine: A dip dye machine allows you to create gorgeous garments. Garment Dip Dyeing Machine The equipment is designed to dye all kinds of woven & knitted wear. And it’s made of high-quality stainless steel. This machine can dye multi-colour products. The lifting operation can be set to automatic or manual control. it is easy to operate & it’s widely used for dyeing sweaters, patterned yarns, or shirts and pants of various colors.

Fig: Dip dyeing machine
- Roll dyeing machine: The machine is suitable for wool, polyester, nylon, rayon, knitwear, etc. dyeing processing. The dyeing machine roller allows you to create gorgeous garments. Ideal for producing garments like dresses and t-shirts, these machines can be configured to handle almost any designs, while speeding up production processes.

Fig: Roll dyeing machine
- Pad dyeing Machine: The pad dyeing machines overcome the deficiency of winch and jigger dyeing machines of smaller batch size and discontinuity in dyeing. Padding mangle offers a continuous process of the fabric in the concerned liquor, such as pretreatment, dyeing, or finishing.
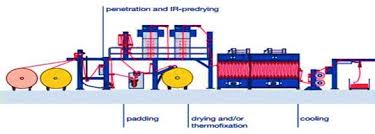
Fig: Pad dyeing Machine
- Loose stock dyeing machine: Loose stock dyeing is most often used these days as a pre-coloration method in the production of woolen-spun yarns in the carpet manufacturing industry where large lots of up to 12 tonnes per color are produced.

Fig: loose stock dyeing machine
- Cop/Cheese dyeing machine: The type of dyeing machine where the cop/ cheese form of yarn is dyed. Here, cop or cheese is directly dyed on a cylinder. It is a type of hank dyeing machine.
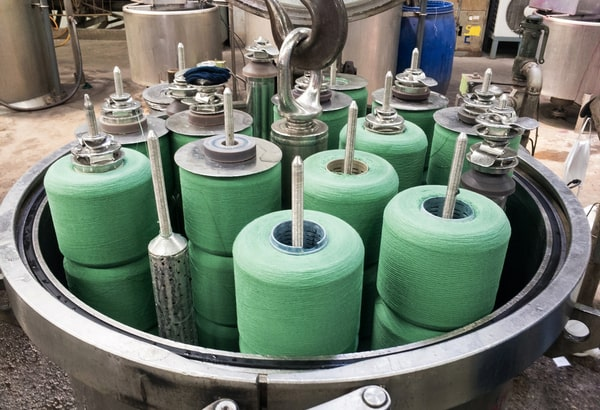

Fig: Cop dyeing machine
- Warp the dyeing machine: The invention discloses a warp dyeing machine, which comprises an electric control system, a heat supply system, a water supply system, a power system, a frame, and a dip dyeing system.

Fig: Warp dyeing machine
- Rotary Printing Machine: A rotary printing press is a printing press in which the images to be printed are curved around a cylinder. Printing can be done on various substrates, including paper, cardboard, and plastic. Substrates can be sheet-fed or unwound on a continuous roll through the press to be printed and further modified if required.

Fig: Rotary printing machine
- Flatbed Printing Machine: Flatbed digital printing is a large-format inkjet printing technology that extends beyond standard inkjet capabilities. It allows for printing on a wide variety of substrates not typically associated with standard inkjet printers. These materials range from plastic, paperboard, ceramic tile, acrylic, fabric, and wood.

Fig: Flatbed printing Machine
- Ink-Jet printing Machine: An Inkjet Printing System is a machine that places marks on products and packaging by projecting a jet of ink onto the surface of the target. Inkjet coders can print on virtually any substrate material, including paper, plastic, wire, cable, metal, resin, glass, and more.

Fig: Inkjet printing machine
- Digital Printing Machine: Digital printing differs from traditional, analog printing methods – such as offset printing – because digital printing machines do not require printing plates. Instead of using metal plates to transfer an image, digital printing presses print the image directly onto the media substrate.

Fig: Digital Printing machine
- Sublimation Printing Machine: Sublimation printing is a digital printing process that uses heat and pressure to transfer dye onto different materials. Here’s the full process: You print a design onto special transfer paper using sublimation inks. Then, you place the paper onto a product and heat it with a heat press.
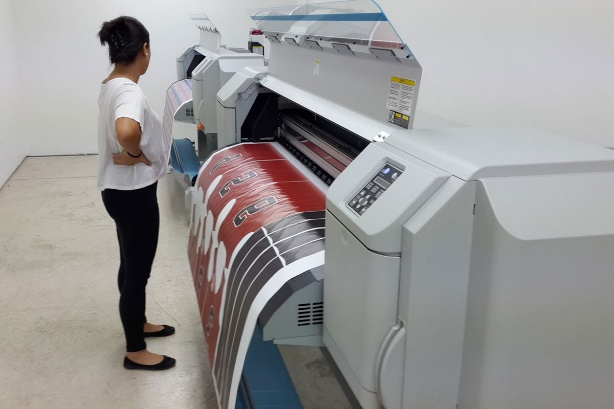

Fig: Sublimation Printing
- Laser Printing Machine: A laser printer is a popular type of computer printer that uses non-impact photocopier technology where no keys are striking the paper. When a document is sent to the printer, a laser beam “draws” the document on a selenium-coated drum using electrical charges.

Fig: Laser Printing Machine
- Mb Printing Machine: The MB Series 4-inch industrial printers feature the best print quality TSC offers thanks to faster processors and upgraded firmware. It can be used for getting the printouts of important documents. To prepare projects in schools or colleges. To print books. To print the hardcopy of presentation in business or companies.

Fig: Mb Printing Machine
- Screen Printing Machine: Screen printers use a silkscreen, a squeegee, and hinge clamps to screen print their designs. The ink is forced through the mesh using the rubber squeegee, the hinge clamps keep the screen in place for easy registration. A. Ink. Screen printing is a process where ink is forced through a mesh screen onto a surface. Making certain areas of the screen impervious to printing ink creates a stencil, which blocks the printing ink from passing through the screen. The ink that passes through forms the printed image.

Fig: Screen printing Machine
- DTF printing machine: Direct-to-film (DTF) printing is a heat-transfer-based print process. The process begins by printing designs onto a transfer film, which is then covered with a thermo-adhesive powder and transferred with a heat press to the final substrate.

Fig: DTF Printing Machine
- Digital Foil Printing Machine: Digital foil printing with a desktop machine replaces hot foil stamping machines and other costly methods for easy and profitable short runs. Digital foiling machines are mainly designed for short runs or single, personalized productions.

Fig: Digital Foil Printing Machine
First Part: Link https://www.textileengineers.org/different-types-of-machines-used-in-the-textile-industry-part-1/#google_vignette
Writer Information
Md Abrar sadman Arpon
Leader, Content Writing Team
Textile Engineers Society
Department of Textile Engineering, JUST


