It is the new upcoming fiber in the world of textile and fashion. The lotus plant yields a unique and rare material known as lotus fiber.It is completely natural and biodegradable. lotus fibre does not harm the environment and completely renewable. Lotus fiber extracted from the stems of lotus which grow naturally on lake especially on Lake-inle and Burma lake. Nelumbo nucifera is the binomial name of lotus. Around 250 meter of thread can be produced by a spinner in a day and 4000 lotus are required to make 1 meter of fabric. All parts of lotus like-leaves, flower, seeds, and stems are used for edible and medical purposes as well as clothing purpose. This is the fiber that is the nano-fiber from nature that’s why it is called eco-friendly fiber. It is antibacterial and self-cleaning as well as super-hydrophobic quality containing plant. Lotus plants are pure by virtue, and they radiate this purity through their fibers. By wearing lotus fiber fabrics, one feels calm, peaceful and meditative. It also cures the wearer from headaches, heart ailments, asthma, and lung issues. The fabric is 100% organic.
Species of lotus fibre are:
1. Nelumbo lutea: new world ( North America)
2. Nelumbo nucifera: old world (Asia and Australia)
Other species:
1. N. flavescens-strongly scented lemon yellow
2. N. alba-bold and beautiful
Structure of lotus fiber:
It is consists of cellulose, hemicelluslose, fat, wax, lignin, ash, pectin, amino acids . The especial ingredient in lotus fiber is cellulose. Cross of fiber is round or oval.
History of lotus fiber:
Lotus is considered as a very spiritual plant and the motif of lotus flower is a very popular design in textiles. Among many religions Hinduism and Buddhism has a strong religion connection with lotus plant. In older day, combodian monks belived to wear lotus fabric as a symbol of peaceful living, purity and divinity. It is very popular in Myanmar and Thailand. It’s a luxurious fabric, with high production time.
with the look and feel of silk-linen combination. Extracting lotus fiber from the lotus stem have been practice in 1910.The development of the lotus roof fabric is only woven in one spot, kaying kan village at the southern tip of Inle Lake in Mayanmar. Lotus weaving was invented by an ethnic Intha woman named Sa Oo in the village of Kyaingkhan in the early 1900s. She first wove a Buddhist monastic robe using lotus fibers, called kya thingan as an offering to the abbot of a local monastery, and offered similar monastic robes to the principal Buddha images at Phaung Taw Oo Pagoda. The tradition of robe-weaving has a long history in Myanmar; during the Tazaungdaing festival, robe-weaving competitions are held throughout major Burmese pagodas.
Also In 2017, plan Thi Thuan, a weaver near Hanoi, introduced the weaving practice to Vietnam. And in 2019, Bijiyashanti Tongbram from Manipuri, India, produced lotus silk from collecting lotus stem from Loktak Lake.
Types of Lotus fiber:
There are 2 types of lotus fiber
1. Seed head lotus fiber
2. Stem lotus fiber
Seed head lotus fiber: Farmers hand harvest the seed pods of the lotus flower to extract fiber, producing seed head lotus fiber using traditional methods in southeast Asia.
Stem lotus fiber: The lotus plant produces stem lotus fiber from its long, thin stems. It is used in textile. It is possible to create a softer texture by combining seed head and stem fibers. And it is enough strong to create a clothing.
Process of fiber making:
Gathering
Knife cut
Twisting
Drawn and rolled
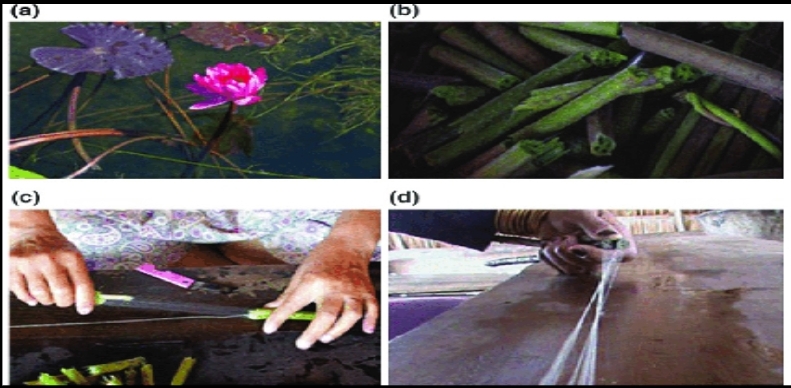
Gathering: Firstly the stems of lotus plant are collected from the lake when it was in full bloom. Deep pink flower contain the best quality fiber.
Knife cut: Take the stems bunchers and mark a slight cut around them by knife.
Twisting: After the slight cut around the stems that are pulled and broken in to the parts.
Drawn and rolled: Twist to expose fibers and windup on a role in the form of yarn.
Yarn preparation:
Placing skeins on bamboo spinning frame.
Than transferring the thread onto winders for warping process.
To avoid tangling, yarn for warp is coiled into plastic bags.
Yarn for weft is wound onto small bamboo bobbins.
Raw lotus threads are a neutral creamy color, natural dyes are used to color the fabric.
Weaving:
1. Cambodian loom are use
2. Width of the cloth is 60-75cm
3. Fabric is woven in 100yds batches
4. Fibers from 120000 lotus stem is used to weave the fabric for a costume.
5. A spinners can produce up to 250 meters of thread a day.
6. Around 30 kg of stems is needed to produce 250 meters of thread.
7. A experimented weaver can weave 1 meter of lotus fabric a day.
Properties:
1. It has the resistance towards pilling
2. Its appearance is raw silk or linen
3. It has the color of milky yellow
4. It has the property of self cleaning
5. It is stiff, cool, lightweight, wrinkle free, stain resistant, crease resistance, water proof, soft, smooth, finer ,sustainable and environment friendly
6. The fineness of single fiber is 3.963 to 4.516 micro meter
7. Initial modulus is 146.81 cn/dtex
8. Elongation at break is 2.75%
9. Density of lotus fiber is 1.1848 g/cc
10. The ratio of length to fineness is about 104
11. Linear density of lotus fiber is 1.55dtex
12. The moisture regain of lotus fiber is 12.32%
13. The crystallinity of lotus fiber is 48.50%
14. It is aur permeable and comfortable
15. It has good elasticity
16. It dries fastly
17. It is cool in summer and warm in winter
Application of lotus fiber:
Lotus fibre is used to make high-quality textiles, including clothing, scarves, and shawls. The fabric is lightweight, breathable, and has a soft, silky texture. Because of its healing properties it also used health and nutrition.
Medicinal uses of lotus plant:
For centuries, lotus flower, seed, leave and underground stem are use to make medicine.
Lotus flower are used to stop bleeding.
Lotus seed are used to treat disorders of the digestive tract, including diarrhea.
Seed are used to treat inflammation and skin problems, including acne.
Lotus seed are used to treat cough, when it was mixed with honey.
Lotus Roots Nutrition Facts:
Excellent source of Vitamin C, with 73% RDA per 100g.
Low in fat and no cholesterol.
Provides a number of B complex vitamins and several minerals, along with good amounts of copper and iron.
It has the optimum 1:4 ratio of low in sodium and high in potassium minerals.
- Advantages of lotus fabric:
- A waste(lotus stems) transformed into a quality textile
- No chemical
- No use of polluting energy
- Hand spun
- Hand woven, by traditional Cambodian methods
- Disadvantages of lotus fabric:
- Collection of raw material, spinning and weaving is handmade so the process is time consuming
- It is most expensive fiber and labor intensive
- The yarns should be woven within 24 hours of being extracted to prevent the deterioration.
Future Prospectives of lotus fiber:
The development of this fiber will give the people, to work in the original environment.
The wettability of lotus fiber will attracted a lot of interest and attention in both academia and industry. Such special wettability textile surfaces are demonstrated with self-cleaning, oil or water separation, self healing, uv-blocking, anti-bacterial and flame retardant performances.
The discarded sems of lotus,it can reduce waste production and aid in its management.
Conclusion:
Lotus fiber being an upcoming fiber, it can be used in making unique fabric. It’s a light weight and self cleaning fiber. It is one of the finest aquatic fibers ever weaved. Its appearance is like silk-linen combination. It’s gives a best result when blended with silk, cotton, kapok and banana fibers in a different proportions. Lotus fiber considered as a luxury material and more expensive than other textiles. However it’s sustainable and natural properties make it a promising alternative to synthetic fibres in the fashion industry.
- Information Source:
- https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/9600/lotus-fibre-a-sustainable-textile
- https://soeagra.com/iaast/iaastjune2019/32.pdf
- https://www.textilecoach.net/post/lotus-fibre
- https://www.ecosilky.com.vn/en/what-is-lotus-fiber-types-properties/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lotus_silk
- https://www.ijhssi.org/papers/vol7(12)/Ver-2/K0712027175.pdf
Writer’s Information:
Anowara
Department of Textile Engineering
Green University of Bangladesh (GUB)


